AI摘要:TensorFlow Lite 是 TensorFlow 的轻量级解决方案,用于在移动和嵌入式设备上部署机器学习模型。本文介绍了如何保存和转换 TensorFlow 模型为 TensorFlow Lite 格式,以及如何进行模型推断。此外,还讨论了模型优化技术,包括量化、剪枝和聚类,以减小模型大小、提高运行效率,同时尽量保持模型准确率。最后,展示了如何结合这些优化技术以获得最佳性能。
Powered by AISummary.
模型保存
export_dir = './layer0'
tf.saved_model.save(model,export_dir)模型保存后的问题树结构如下图所示: 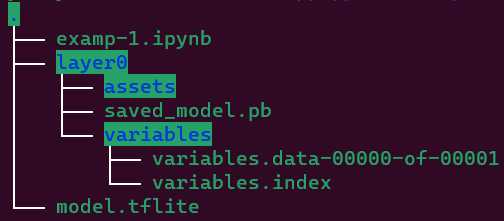
模型转换
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(export_dir)
tflite_model = converter.convert()
import pathlib
tflite_model_file = pathlib.Path('./model.tflite')
tflite_model_file.write_bytes(tflite_model)
模型转换后生成model.tflite。
使用 tf.lite.TFLiteConverter 转换 TensorFlow 2.x 模型。TensorFlow 2.x 模型是使用 SavedModel 格式存储的,并通过高阶 tf.keras.* API(Keras 模型)或低阶 tf.* API(用于生成具体函数)生成。
以下是将 Keras 模型转换为 TensorFlow Lite 模型。
import tensorflow as tf
# Create a model using high-level tf.keras.* APIs
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=1, input_shape=[1]),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=16, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=1)
])
model.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mean_squared_error') # compile the model
model.fit(x=[-1, 0, 1], y=[-3, -1, 1], epochs=5) # train the model
# (to generate a SavedModel) tf.saved_model.save(model, "saved_model_keras_dir")
# Convert the model.
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
tflite_model = converter.convert()
# Save the model.
with open('model.tflite', 'wb') as f:
f.write(tflite_model)`
模型推断
TensorFlow Lite 解释器(interpreter)是一个库(library),它接收一个模型文件(model file),执行模型文件在输入数据(input data)上定义的运算符(operations),并提供对输出(output)的访问。
interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_content=tflite_model)
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_det = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_det = interpreter.get_output_details()输入1个数进行推断。
to_pre = np.array([[1.5]]).astype(np.float32)
interpreter.set_tensor(input_det[0]['index'],to_pre)
interpreter.invoke()
tflite_ret = interpreter.get_tensor(output_det[0]['index'])模型转换后生成model.tflite。
模型优化
将优化推断的复杂性降至最低,降低权重的精确表示,并且可选的降低存储和计算的激活值。
优化可能会导致模型准确率发生变化,这在应用开发过程中必须予以考虑。
准确率的变化取决于被优化的单个模型,而且很难提前预测。一般来说,针对大小或延迟进行优化的模型会损失少量准确率。根据您应用的不同,这可能会或可能不会影响您的用户体验。在极少数情况下,某些模型可能会因为优化过程而获得准确性的小幅提升。
量化
量化的工作原理是降低用于表示模型参数的数字(默认情况为 32 位浮点数)的精度。这样可以获得较小的模型大小和较快的计算速度。
使用 int16 激活的量化是一个具有 int16 激活和 int8 权重的全整数量化方案。与激活和权重均为 int8 的全整数量化方案相比,这种模式可以提高量化模型的准确率,并保持相似的模型大小。建议在激活对量化敏感时使用。

训练后量化
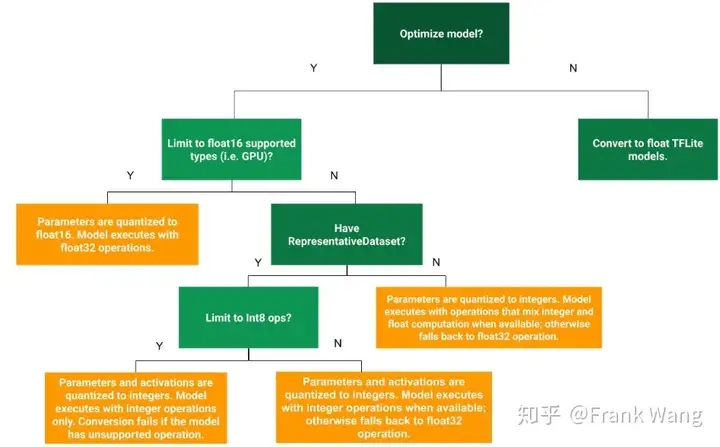
量化权重
权重可能会转换为精度降低的类型,例如 16 位浮点数或 8 位整数。我们通常建议将 16 位浮点数用于 GPU 加速,而将 8 位整数用于 CPU 执行。
import tensorflow as tf
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_dir)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
tflite_quant_model = converter.convert()权重量化为float16,其他为float32。
权重和激活的全整数量化
通过确保量化权重和激活,可以改善延迟、处理时间和功耗,并访问仅支持整数的硬件加速器。这需要一个较小的代表性数据集,通过representative_dataset_gen估算所有可变数据的动态范围。
import tensorflow as tf
def representative_dataset_gen():
for _ in range(num_calibration_steps):
# Get sample input data as a numpy array in a method of your choosing.
yield [input]
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_dir)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset_gen
tflite_quant_model = converter.convert()权重和激活量化为float16,其他为float32,生成的模型仍采用浮点输入和输出。
整数量化
将 32 位浮点数(如权重和激活输出)转换为 8 位定点数。
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.representative_dataset = representative_data_gen
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
converter.inference_input_type = tf.uint8
converter.inference_output_type = tf.uint8
tflite_model_int8_quant = converter.convert()
interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_content=tflite_model_int8_quant)
input = interpreter.get_input_details()
output = interpreter.get_output_details()该模型使用整数数据作为模型的输入和输出张量,因此它兼容仅支持整数的硬件。
float16 量化
将权重转换为 16 位浮点值。
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.target_spec.supported_types = [tf.float16]
tflite_model_float16_quant = converter.convert()
tflite_model_float16_quant_file = tflite_models_dir/"mnist_model_float16_quant.tflite"
tflite_model_float16_quant_file.write_bytes(tflite_model_float16_quant)
interpreter_fp16 = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path=str(tflite_model_float16_quant_file))
interpreter_fp16.allocate_tensors()量化张量的表示
8 位量化近似于使用以下公式得到的浮点值。
$real_value = (int8_value - zero_point) \times scale$
该表示包含两个主要部分:
- 由 int8 补码值表示的逐轴(即逐通道)或逐张量权重,范围为 [-127, 127],零点等于 0。
- 由 int8 补码值表示的按张量激活/输入,范围为 [-128, 127],零点范围为 [-128, 127]。
剪枝
剪枝的工作原理是移除模型中对其预测影响很小的参数。剪枝后的模型在磁盘上的大小相同,并且具有相同的运行时延迟,但可以更高效地压缩。这使剪枝成为缩减模型下载大小的实用技术。
模型剪枝有两种方式,剪神经元,或者剪权重(不破坏原来的网络结构)。剪神经元对模型的影响较大,剪权重对模型的精度影响较小。
一个简单且实践有效的思路是:magnitude-based weight pruning,即按照参数(或特征输出)绝对值大小来评估重要性,《Pruning Filters for Efficient ConvNets》
基于上述这个简单有效的思路,TensorFlow Model Optimization工具包,直接提供了prune_low_magnitude API函数来实现。
微调预训练模型和剪枝
Fine-tune pre-trained model with pruning
batch_size = 128
epochs = 2
validation_split = 0.1
num_img = test_img.shape[0]*(1-validation_split)
end_step = np.ceil(num_img/batch_size).astype(np.int32)*epochsimport tensorflow_model_optimization as tfopt
prune_low_magnitude = tfopt.sparsity.keras.prune_low_magnitude
pruning_params = {
'pruning_schedule':tfopt.sparsity.keras.PolynomialDecay(
initial_sparsity=0.5,
final_sparsity=0.8,
begin_step=0,
end_step=end_step
)
}
model_for_pruning = prune_low_magnitude(model,**pruning_params)prune_low_magnitude修改要在训练期间修剪的tf.keras图层或模型,剪的是权重,对网络构架无影响。
PolynomialDecay提供学习率按多项式衰减的策略。
- 以稀疏性为initial_sparsity,到达到稀疏性为final_sparsity结束。多少稀疏就代表着多少权重将会消失(变成0)。
- 以begin_step为开始,到end_step这个期间,每隔frequency的steps,就修剪一次模型。
- power是多项式衰减系数
按多项式衰减的方式进行权重剪枝。经过剪枝后的参数量多了Non-trainable params参数,这些是不可训练的参数。是tensorflow-model-optimization为网络中的每个权重添加的不可训练掩码,表示是否要修剪该权重,掩码为0或1。
callbacks = [
tfopt.sparsity.keras.UpdatePruningStep(),
tfopt.sparsity.keras.PruningSummaries(log_dir=str(logdir))
]UpdatePruningStep回调,使其在训练过程中处理修剪更新。
PruningSummaries提供用于跟踪进度和调试的日志。
在修剪完模型后,我们需要使用strip_pruning来删除Non-trainable params。使用标准压缩算法对比前后模型的变化。
model_for_export = tfopt.sparsity.keras.strip_pruning(model_for_pruning)聚类
聚类的工作原理是将模型中每一层的权重归入预定数量的聚类中,然后共享属于每个单独聚类的权重的质心值。这就减少了模型中唯一权重值的数量,从而降低了其复杂性,从而带来部署优势。
聚类首先将每层的权重分组成 N 个聚类,然后共享属于相应聚类的所有权重的聚类形心值。
使用cluster_weights()应用于整个预训练模型,压缩后可有效缩减模型大小,还能保持良好的准确率。
cluster_weights = tfopt.clustering.keras.cluster_weights
centroinit = tfopt.clustering.keras.CentroidInitialization
clustering_params = {
'number_of_clusters':16,
'cluster_centroids_init':centroinit.LINEAR
}
cluster_model = cluster_weights(model,**clustering_params)
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-5)
cluster_model_for_export = tfopt.clustering.keras.strip_clustering(cluster_model)
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(cluster_model_for_export)
tflite_cluster_model = converter.convert()
cluster_tflite_file = keras_dir/'mnist_model_cluster.tflite'
cluster_tflite_file.write_bytes(tflite_cluster_model)聚类方法使用CentroidInitialization(中心初始化),使用strip_pruning来删除Non-trainable params,最后转换成tflite模型。
再经过量化处理,继续压缩。
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(cluster_model_for_export)
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
cluster_quant_model = converter.convert()
cluster_quant_tflite_file = keras_dir/'mnist_model_cluster_quant.tflite'
cluster_quant_tflite_file.write_bytes(cluster_quant_model)
interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_content=cluster_quant_model)
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
cluster_test_acc = evaluate_model(interpreter)协作优化
优化方式示意图如下。

优化结果如下图所示。


